Command Line Tools For Mac
- Command Line Tools For Mac
- Macos Command Line Tools Without Xcode
- Xcode Command Line Build
- Update Command Line Tools Mac
Mac users with macOS Mojave and macOS Catalina, and new operating systems in place can now install Command Line Tools from the Xcode IDE without needing to install the entire Xcode package, or opening an Apple developers account.
In this article, we cover how you can install this optional and highly useful Command Line Tools package.
X code 11. Credit: developerinsider
What is the Xcode Command Line Tools package?
For Mac power users — we wouldn't recommend downloading this unless you are comfortable with Terminal — the Xcode Command Line Tools package gives you a complete Unix toolkit accessible through Terminal. No developer account needed and you don't need to download the entire — and quite large Xcode package of executables.
- Using Launchpad: Open Launchpad. It’s the silver icon in the Dock that looks like a rocket.
- The AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) is a unified tool to manage your AWS services. With just one tool to download and configure, you can control multiple AWS services from the command line and automate them through scripts. The AWS CLI introduces a new set of simple file commands for efficient file transfers to and from Amazon S3.
- In OS X 10.9, the Downloads pane of Xcode Preferences does not support downloading command-line tools. Use any of the following methods to install command-line tools on your system: If Xcode is installed on your machine, then there is no need to install them. Xcode comes bundled with all your command-line tools.
Within the Xcode Command Line toolkit, Mac users gain access to numerous useful tools, utilities, and compilers, including make, GCC, clang, perl, svn, git, size, strip, strings, libtool, cpp, and many others. All of these commands are a default part of Linux systems and programs.
Install Azure CLI on macOS.; 3 minutes to read +4; In this article. For the macOS platform, you can install the Azure CLI with homebrew package manager.Homebrew makes it easy to keep your installation of the CLI update to date. To install the necessary Xcode tools using Xcode on the Mac: Start Xcode on the Mac. Choose Preferences from the Xcode menu. In the General panel, click Downloads. On the 'Downloads for Apple Developers' list, select the Command Line Tools entry that you want.
We recommend following these steps for those with the following operating systems running on a Mac: macOS 10.13 High Sierra, macOS 10.14 Mojave, and macOS 10.15 Catalia onward. It isn't always possible to download these Xcode Command Line Tools, following these steps, on Mac’s running older operating systems. Other ways to install command tools and gcc (without needing Xcode) is available through the Apple Developer website.
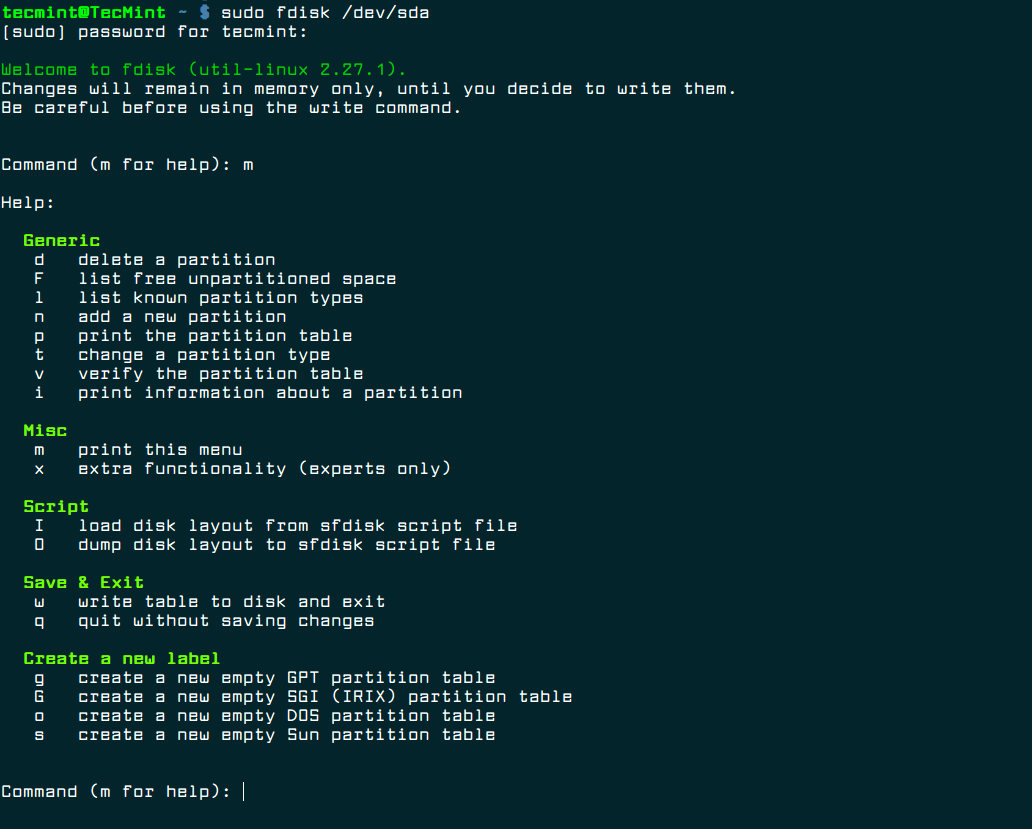
Here is how you install Xcode Command Line Tools.
How to install Xcode Command Line Tools?
- Go to Terminal in /Applications/Utilities/.
- Input the following command string in Terminal:
xcode-select —install - In the same way when you are downloading new software and apps, a popup update window will appear asking you: “The xcode-select command requires the command line developer tools. Would you like to install the tools now?”
- Select confirm by clicking Install.
- Wait for the Xcode Command Line Tools package to install. It is around 130 MB and usually installs fairly quickly; although it depends on your connection.
- Once everything is installed, the installer goes away and you should be able to any of the new commands that you’ve now got access to. Enjoy using your new Unix command line tools!
With this new download, you should have access to 61 Unix command line tools. For example, one of the advantages of having these tools is you can install new apps and software directly from the source code instead of needing to go through the package manager and usual download route.
To access or view everything you've now got, go to the following directory:
/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/
Please note, this is the root /Library of your macOS/OS X, not the ~/Library directory.
All of these tools can also be found in: /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/usr/bin/
What happens if I encounter problems downloading these?
If you get an error message that says “Can’t install the software because it is not currently available from the Software Update server”, it means you've already got the Xcode package on your Mac. Mac OS X 10.9 onward, Xcode was already installed, which is why you aren't able to download these tools. However, what you can do is uninstall the entire Xcode app if you'd prefer to only access these tools and not a whole load of software that isn’t going to be of much use.
Watch out for Xcode junk
The Xcode junk is one of those types of clutter that is keeps accumulating in remote places on your Mac. It could take up a few gigs of your space. The only app that seems to address this problem is CleanMyMac X by MacPaw. It’s loved by many Mac developers because it collects those specific types of development junk, like Xcode or outdated libraries.
Once you launch the app, click on System Junk > Scan. Then, click “Review Details”
CleanMyMac X is a powerful Mac performance improvement app. It makes your Mac as good as new. Let it scan your system and clear out any unwanted Xcode, development and system junk that is taking up too much space and cluttering up your Mac. In a few clicks, your Mac could be running smoother, quicker and more efficiently.
The AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) is a unified tool to manage your AWS services. With just one tool to download and configure, you can control multiple AWS services from the command line and automate them through scripts.
The AWS CLI v2 offers several new features including improved installers, new configuration options such as AWS Single Sign-On (SSO), and various interactive features.
Windows
Download and run the 64-bit Windows installer.
MacOS
Download and run the MacOS PKG installer.
Linux
Download, unzip, and then run the Linux installer
Amazon Linux
The AWS CLI comes pre-installed on Amazon Linux AMI.
Release Notes
Check out the Release Notes for more information on the latest version.
aws-shell is a command-line shell program that provides convenience and productivity features to help both new and advanced users of the AWS Command Line Interface. Key features include the following.
Command Line Tools For Mac
- Fuzzy auto-completion for
- Commands (e.g. ec2, describe-instances, sqs, create-queue)
- Options (e.g. --instance-ids, --queue-url)
- Resource identifiers (e.g. Amazon EC2 instance IDs, Amazon SQS queue URLs, Amazon SNS topic names)
- Dynamic in-line documentation
- Documentation for commands and options are displayed as you type
- Execution of OS shell commands
- Use common OS commands such as cat, ls, and cp and pipe inputs and outputs without leaving the shell
- Export executed commands to a text editor
To find out more, check out the related blog post on the AWS Command Line Interface blog.
The AWS Command Line Interface User Guide walks you through installing and configuring the tool. After that, you can begin making calls to your AWS services from the command line.
You can get help on the command line to see the supported services,
New file commands make it easy to manage your Amazon S3 objects. Using familiar syntax, you can view the contents of your S3 buckets in a directory-based listing.
You can perform recursive uploads and downloads of multiple files in a single folder-level command. The AWS CLI will run these transfers in parallel for increased performance.
A sync command makes it easy to synchronize the contents of a local folder with a copy in an S3 bucket.
Macos Command Line Tools Without Xcode
See the AWS CLI command reference for the full list of supported services.
Xcode Command Line Build
Connect with other developers in the AWS CLI Community Forum »
Find examples and more in the User Guide »
Learn the details of the latest CLI tools in the Release Notes »
Update Command Line Tools Mac
Dig through the source code in the GitHub Repository »
